Abstract:
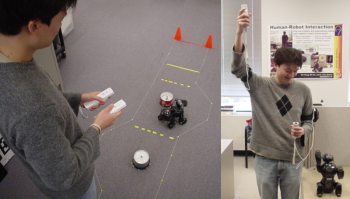
we suggest the use of tangible user interfaces (TUIs) for human-robot interaction (HRI) applications. We discuss the potential benefits of this approach while focusing on low-level of autonomy tasks. We present an experimental robotic interaction testbed we implemented to support our investigation. We used the testbed to explore two HRI-related task-sets: robotic navigation control and robotic posture control. We discuss the implementation of these two task-sets using an AIBO robot dog. Both tasks were also mapped to two different robotic control interfaces: keypad interface which resembles the interaction approach common in HRI, and a gesture input mechanism based on Nintendo Wiimotes and Nunchuks. We discuss the interfaces implementation and conclude with a detailed user study we performed to compare these different HRI techniques in the two robotic tasks-sets.
Researchers: Cheng Guo, Ehud Sharlin
- Publications:
- C. Guo and E. Sharlin, “Exploring the Use of Tangible User Interfaces for Human-Robot Interaction: A Comparative Study”, Human Factors in Computing Systems, ACM CHI 2008, Best Paper Award Nominee, pp. 121-130, Florence, Italy, April 2008.
- C. Guo and E. Sharlin. “Exploring the Use of Tangible User Interfaces for Human-Robot Interaction: A Comparative Study”. Departmental Technical Report 2007-880-32, September 25, 2007, Department of Computer Science, University of Calgary, AB, Canada, 2007.